Inside-the-body immunoregulatory platform technology using the characteristics of γ-PGA,
a new immunity-controlling material for medicine
HumaMAX®
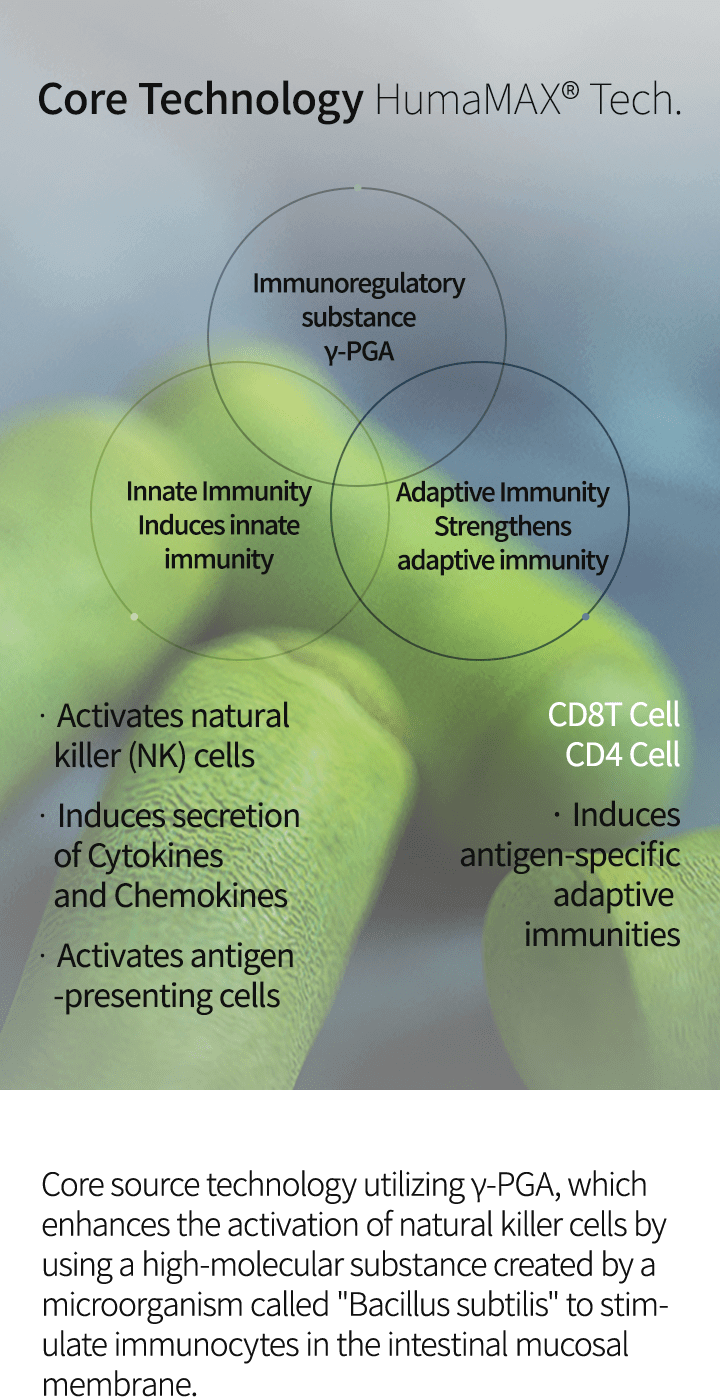
Core source technology utilizing γ-PGA, which enhances the activation of natural killer cells by using a high-molecular substance created by a microorganism called "Bacillus subtilis" to stimulate immunocytes in the intestinal mucosal membrane.
New medicine development platform technology based on the immunoregulatory effects of a natural amino acid high-molecular refined substance, "γ-PGA (Poly-γ-glutamic Acid)"
- A structure in which glutamic acid, a necessary type of amino acid, is repetitively connected through gamma-peptide bonds
- Its mechanism is an immunoregulatory effect : TLR4 as a medium ① Induces innate immunity ② Strengthens adaptive immunity ③ Improves the tumor microenvironment (TEM) in a favorable manner
"Bacillus subtilis Chungkookjang," a GRAS (Generally recognized as safe) microorganism
- Produced with a patented strain
Medicine under development and diseases to be treated
- Extended application for more diseases : A combined treatment of tumor with Immune Checkpoint Blockade (ICB), cell therapy products, etc.
Poly-γ-glutamic acid (γ-PGA)

- An edible amino acid, high-molecular material, and a natural substance found in bean-fermented foods such as Korea's very own
"cheonggukjang" - Produced by Bacillus subtilis Chungkookjang, a type of GRAS (generally recognized as safe) microorganism with edible safety established
(BioLeaders' patented strain) - Though it is a natural substance, a mass production system for γ-PGA of high molecular weight (2,000 kDa on average) has been established
through a fermentation and refinement processes (certified as one of Korea's Top 10 New Technologies) - Increase in immunoreaction via γ-PGA, effective against cancer, viruses, and inflammation diseases
- γ-PGA also has several health-related functions including moisturization, acceleration of mineral absorption, and inhibited activation of
the lyase of hyaluronic acid, which is a tissue component inside the body
Oral administration

- High Stability and ease of administration
- Absorption in the small intestine via oral dosing
- Activation of dendritic cells and dendritic cells, which are immune cells in the small intestine mucosa
Increased immune response
by poly-gamma glutamic acid
- Anticancer effect
- antiviral effect
- Inflammatory disease inhibitory effect
Innate immunity
- γ-PGA enhances innate immune function through intestinal mucosa cells
- Enhance immune function by activating immune cell (marcrophage) and natural killer cells (NK cells) that maintain immune function in vivo
- Antigen-presenting cell activation
Adaptive immunity
- increased immune response
by inducing maturation
of immature dendritic cells